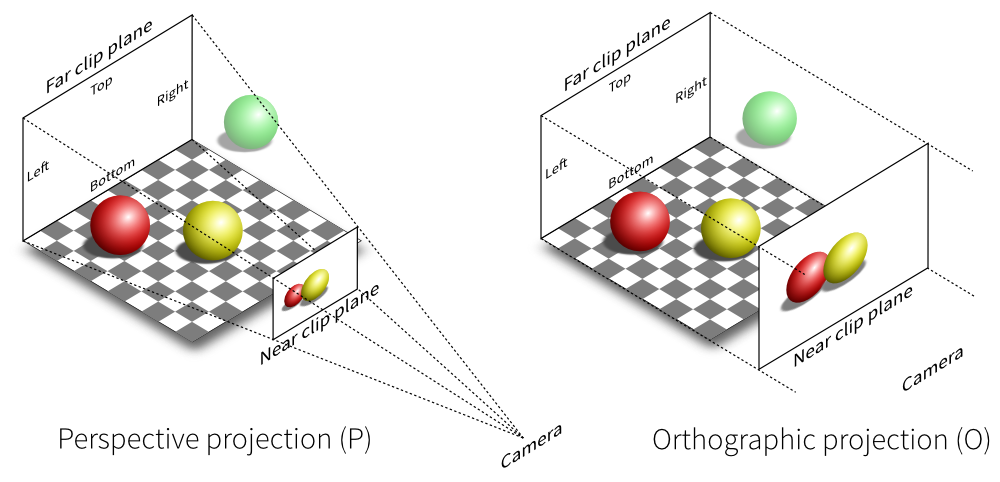
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T, size_t size>
struct MemoryPool {
T buf[size], *tail;
T *st[size];
int top;
MemoryPool() : top(0), tail(buf) {}
inline T *alloc() {
return top ? st[--top] : tail++;
}
inline void recycle(T *p) {
st[top++] = p;
}
};
struct ScapegoatTree {
static const double alpha = 0.75;
static const int MAXN = 100010;
struct Node {
Node * ch[2];
int key, size, cover;
bool exist;
inline void update() {
size = ch[0]->size + ch[1]->size + (int)exist, cover = ch[0]->cover + ch[1]->cover + 1;
}
inline bool check(void) {
return ((ch[0]->cover > cover * alpha + 5) || (ch[1]->cover > cover * alpha + 5));
}
};
Node *root, *null;
MemoryPool<Node, MAXN> pool;
Node *newNode(int key) {
Node *p = pool.alloc();
p->ch[0] = p->ch[1] = null, p->size = p->cover = 1, p->exist = true, p->key = key;
return p;
}
inline void travel(Node *p, std::vector<Node *> &v) {
if (p == null) return;
travel(p->ch[0], v);
if (p->exist) v.push_back(p);
else pool.recycle(p);
travel(p->ch[1], v);
}
inline Node *divide(std::vector<Node *> &v, int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return null;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
Node *p = v[mid];
p->ch[0] = divide(v, l, mid);
p->ch[1] = divide(v, mid + 1, r);
p->update();
return p;
}
inline void rebuild(Node *&p) {
static std::vector<Node *> v;
v.clear(), travel(p, v), p = divide(v, 0, v.size());
}
inline Node **insert(Node *&p, int val) {
if (p == null) {
p = newNode(val);
return &null;
} else {
p->size++, p->cover++;
Node **res = insert(p->ch[val >= p->key], val);
if (p->check()) res = &p;
return res;
}
}
inline void erase(Node *p, int id) {
p->size--;
register int offset = p->ch[0]->size + p->exist;
if (p->exist && id == offset) {
p->exist = false;
return;
} else {
if (id <= offset) erase(p->ch[0], id);
else erase(p->ch[1], id - offset);
}
}
ScapegoatTree() {
null = pool.alloc();
null->ch[0] = null->ch[1] = null;
null->cover = null->size = null->key = 0;
root = null;
}
inline void insert(int val) {
Node **p = insert(root, val);
if (*p != null) rebuild(*p);
}
inline int rank(int val) {
Node *p = root;
register int ans = 1;
while (p != null) {
if (p->key >= val) p = p->ch[0];
else {
ans += p->ch[0]->size + p->exist;
p = p->ch[1];
}
}
return ans;
}
inline int select(int k) {
Node * p = root;
while (p != null) {
if (p->ch[0]->size + 1 == k && p->exist) return p->key;
else if (p->ch[0]->size >= k) p = p->ch[0];
else k -= p->ch[0]->size + p->exist, p = p->ch[1];
}
}
inline void erase(int k) {
erase(root, rank(k));
if (root->size < alpha * root->cover) rebuild(root);
}
inline void eraseByRank(int k) {
erase(root, k);
if (root->size < alpha * root->cover) rebuild(root);
}
};
inline char read(void) {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
if (p1 == p2) {
p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin);
if (p1 == p2) return EOF;
}
return *p1++;
}
inline void read(int &x) {
static char c; c = read(); int b = 1;
for (x = 0; !isdigit(c); c = read()) if (c == '-') b = -b;
for (; isdigit(c); x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ '0'), c = read()); x *= b;
}
ScapegoatTree tree;
int n, k, m;
int main(void) {
read(n);
while (n--) {
read(k), read(m);
switch (k) {
case 1: tree.insert(m); break;
case 2: tree.erase(m); break;
case 3: printf("%d\n", tree.rank(m)); break;
case 4: printf("%d\n", tree.select(m)); break;
case 5: printf("%d\n", tree.select(tree.rank(m) - 1)); break;
case 6: printf("%d\n", tree.select(tree.rank(m + 1))); break;
}
}
return 0;
}
|